
Quality Assurance
Diligence, processes, and attention to detail are at the core of our business. Setting the quality standard in electronic components distribution.
Quality Assurance
ChipTop have warehouses and quality control management centers both in Shenzhen and Hong Kong. Also, we have established strategic partnerships with professional
testing organizations to provide assurance for quality control throughout the entire process. Whether you’re in consumer electronics or a high-reliability environment,
your products — and business — depend on quality electronic components. Our strictly quality-control process ensures the integrity of every electronic
component we distribute.
Professional third-party test lab test selection
-
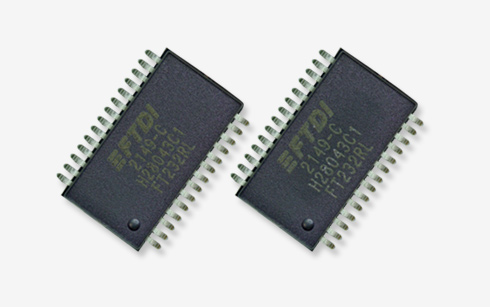
External visual inspection
The aim of an EVI (external visual inspection) is to verify the conformity of the exterior of electrical, electronic and electromechanical components (EEE parts) with the acquisition document. The following aspects should be considered:
• Marking
• Aspect of Materials
• Workmanship
• Pins
• Sealing -
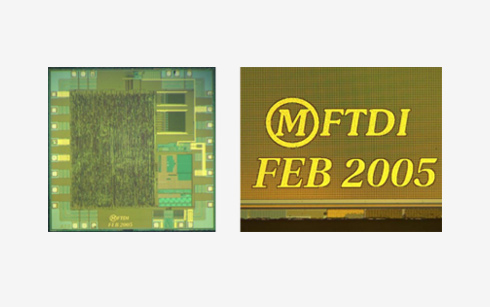
Internal Visual inspection
These processes are called “destructive” as they render the components unusable afterward. The first destructive method is called encapsulation. This involves placing abrasive acids on the surface of the component until the internal dye reveals itself, which can then be inspected with a microscope. If the component is made from ceramic packaging, the lid can be manually removed in a similar process called de-cap.
In the case of blacktopping, one destructive test calls for acetone to be applied to the top of the chip package, usually with a cotton swab. If residue from the chip comes off, the chip is a no-go. You can also perform a scrape test, which can determine if a clear coat was used to hide the use of blacktop. 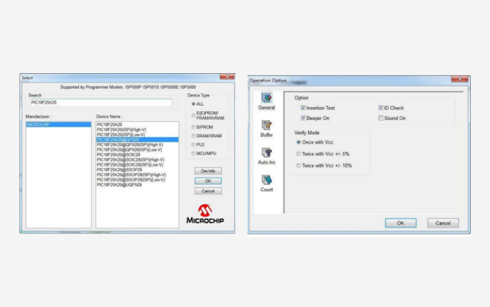
Memory Test
Memory test is the process of testing the functionality of the memory blocks in an IC during the manufacturing test. Memory testing is performed using dedicated DFT instruments that generate test patterns applied to the memory under test and then compare the stored data with the expected results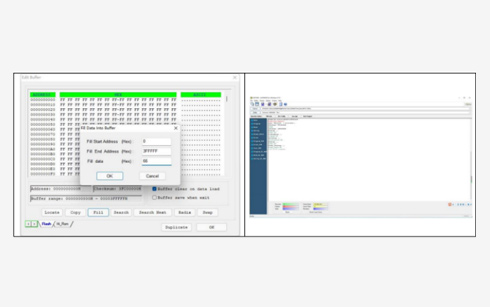
Programming test
IC programming, also known as “programming” or “burning,” is the process of transferring the program or firmware into the internal storage space of an Integrated Circuit (IC) or microchip. This critical step is essential to enable the chip to perform its designated functions and tasks within electronic devices.
IC Programming Verification Steps:
• Place the IC that requires programming into the socket and burn it according to the work instruction.
• After successful programming, place the IC into other sockets with different numbers and run the verification process (“VERIFY”).
• Check the results to ensure the programming socket’s functionality.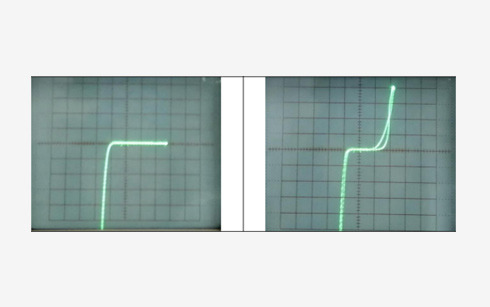
Solderability test
Solderability testing is a destructive test and a common flow-down requirement performed to ensure that the solder will stick to the leads properly in next level assembly. A proper solder connection indicates proof of wetting and is a reliable and quantitative way to measure solderability. Wetting balance evaluates the speed and adhesion strength between molten solder and the test surfaces. Wetting is influenced by the type of metal used or any contaminants on the surface. Wetting balance will differ for through-hole (TH) and surface-mount (SM) components but both are based on the same physical principals.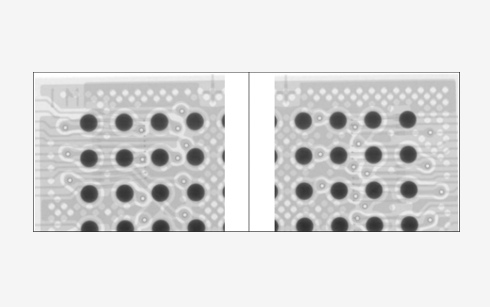
X-ray
Components can be tested with X-ray inspection to verify their authenticity. As its name suggests, this process works just like a normal X-ray and allows you to view the internal contents of the part. This process can identify indicators like:
• Missing or inconsistent die sizes
• Visible delamination
• Broken or missing wire bonds
If the part is RoHS-approved, X-ray inspection can be used to confirm its lead-free status, something that counterfeiters often overlook.

